
In the digital age, we have witnessed a transformation in nearly every aspect of our lives, from how we communicate to how we shop, work, and socialize. This transformation, while bringing numerous benefits, has also introduced a new range of threats. One of the most pressing concerns in today’s interconnected world is cybercrime. The term encompasses a wide variety of criminal activities that target digital systems, networks, and devices. Cybercrime is not only a growing concern for individuals but also for businesses, governments, and society at large.
In this blog, we will explore the nature of cybercrime, its various forms, the impact it has on individuals and organizations, and the efforts being made to combat it. We will also look at the legal landscape surrounding cybercrime and provide practical advice on how to protect yourself from becoming a victim.
What is Cybercrime?

Cybercrime refers to any criminal activity that involves a computer, network, or electronic device. While the definition can vary depending on jurisdiction, it generally involves crimes where the internet or other digital technologies are used to commit illegal activities. These crimes may target individuals, organizations, or governments and can range from identity theft and fraud to hacking and cyberterrorism.
Cybercriminals are individuals or groups who exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems, often for financial gain, political motives, or personal vendettas. The rapid growth of the internet and technology has provided them with an ever-expanding playground, and as technology continues to evolve, so too do the methods employed by cybercriminals.
Categories of Cybercrime
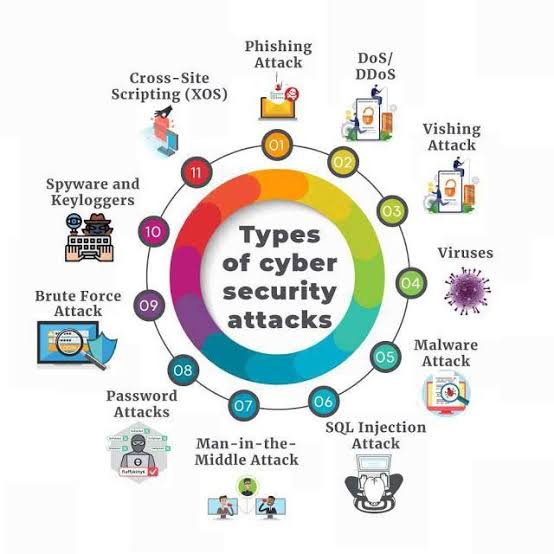
Cybercrime can be broadly classified into several categories, based on the type of activity involved and the target of the crime. Some of the most common categories include:
1. Hacking
Hacking is one of the most well-known forms of cybercrime. It involves unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or data. Hackers may breach a system for a variety of reasons, including stealing sensitive information, disrupting services, or testing system vulnerabilities. While some hackers engage in hacking for fun or as a challenge, others do so with malicious intent, such as stealing financial data or deploying ransomware.
Types of Hacking:
- Black Hat Hacking: Malicious hacking for personal or financial gain.
- White Hat Hacking: Ethical hacking, typically performed by security experts to identify vulnerabilities and help strengthen systems.
- Grey Hat Hacking: A mix of both ethical and unethical hacking, where hackers may exploit vulnerabilities but report them afterward.
2. Phishing
Phishing is a method of cybercrime where attackers impersonate legitimate entities, such as banks, businesses, or government organizations, in order to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or social security numbers. Phishing attacks often occur through email, text messages, or fake websites.
There are several types of phishing attacks:
- Spear Phishing: Targeted attacks aimed at specific individuals or organizations.
- Whaling: A more sophisticated form of phishing that targets high-level executives or important figures within an organization.
3. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible, and demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. This form of cybercrime has become increasingly prevalent in recent years, with attacks on both individuals and large organizations.
Ransomware attacks can have devastating consequences, particularly for businesses, as they can lead to data loss, financial losses, and reputational damage. High-profile ransomware attacks on healthcare organizations, municipalities, and global corporations have highlighted the severity of this crime.
4. Identity Theft
Identity theft occurs when cybercriminals steal personal information, such as social security numbers, credit card information, or bank account details, and use it to impersonate the victim for fraudulent purposes. Identity theft can have long-lasting effects on victims, including damage to credit scores, financial losses, and emotional distress.
With the rise of online shopping and digital services, identity theft has become a growing concern. Cybercriminals can obtain personal information through hacking, phishing, or even data breaches.
5. Cyberbullying and Online Harassment
Cyberbullying involves using digital platforms to harass, intimidate, or threaten others. It can take many forms, including sending abusive messages, spreading rumors, or engaging in online stalking. The anonymity of the internet allows perpetrators to harass their victims without fear of immediate consequences.
Cyberbullying can have severe psychological effects on the victims, particularly among children and teenagers. The rise of social media platforms has made it easier for cyberbullies to target individuals, and the impact of these attacks can be long-lasting.
6. Online Fraud
Online fraud refers to any fraudulent activity that takes place on the internet. This includes activities such as credit card fraud, auction fraud, investment scams, and fake online stores. Cybercriminals often use deceptive tactics to convince victims to part with their money, whether through fake websites, false promises of investment returns, or fake products and services.
One of the most common forms of online fraud is e-commerce fraud, where criminals use stolen credit card information to make unauthorized purchases from online retailers.
7. Cyberterrorism
Cyberterrorism refers to the use of digital technology and the internet to carry out attacks intended to cause fear, disrupt critical infrastructure, or further a political agenda. These attacks can target government systems, energy grids, financial institutions, or other vital infrastructure. While cyberterrorism is still a relatively new phenomenon, it poses a significant threat to national security and public safety.
The potential for widespread damage and chaos makes cyberterrorism a serious concern for governments around the world. Attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power plants or hospitals, could have catastrophic consequences.
The Impact of Cybercrime

The effects of cybercrime are far-reaching and can have serious consequences for individuals, organizations, and even entire nations. While the financial losses from cybercrime are the most immediate and tangible impacts, there are also long-term and more intangible effects.
1. Financial Losses
Cybercrime is a multi-billion-dollar industry, with criminals targeting individuals, businesses, and governments for financial gain. According to estimates, cybercrime costs the global economy trillions of dollars each year. These losses may stem from fraud, theft of intellectual property, or the costs associated with data breaches and ransomware attacks.
For individuals, financial losses may include stolen credit card information, unauthorized purchases, or the cost of repairing damaged financial reputations. For businesses, the costs of cybercrime can be far greater, ranging from lost revenue and legal expenses to the costs of restoring data and repairing damage to brand reputation.
2. Reputational Damage
For businesses, the reputational damage from a cyberattack can be devastating. A high-profile data breach, particularly one that involves customer data, can erode trust in a company and lead to a loss of business. Customers are increasingly concerned about the security of their personal information, and a breach can result in customer churn, decreased sales, and damage to long-standing relationships.
For individuals, the effects of identity theft or online harassment can have long-lasting emotional and psychological effects, leading to a loss of confidence and security.
3. Emotional and Psychological Impact
Cybercrimes like online harassment and identity theft can have serious emotional and psychological consequences for victims. Individuals who experience cyberbullying may suffer from anxiety, depression, and even suicidal thoughts. The sense of helplessness and violation that comes with identity theft or fraud can also leave long-lasting scars.
4. National Security Threats
On a larger scale, cybercrime has the potential to undermine national security. Cyberattacks targeting government agencies or critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and financial institutions, could cause widespread disruption. Such attacks may be carried out by state-sponsored actors, organized cybercriminal groups, or even lone hackers with political or ideological motives.
Combating Cybercrime

Efforts to combat cybercrime involve a combination of technological solutions, legal frameworks, law enforcement cooperation, and public awareness. As cybercrime continues to evolve, so too must the strategies used to fight it.
1. Cybersecurity Measures
At the core of any anti-cybercrime strategy is robust cybersecurity. This involves the use of technical measures to protect digital systems from attacks. Organizations and individuals must take steps to safeguard their data and devices by using firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and antivirus software.
For businesses, implementing strong cybersecurity policies, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and training employees in cybersecurity best practices are essential steps in reducing the risk of a cyberattack.
2. Law Enforcement and International Cooperation
Cybercrime often transcends national borders, making it difficult for any one country to combat it alone. International cooperation between law enforcement agencies is critical in tackling cybercriminal activity. Organizations like INTERPOL, Europol, and the FBI collaborate with countries worldwide to track down cybercriminals and dismantle criminal networks.
Cybercrime units within police forces are becoming more specialized, and governments are increasingly focusing on developing legislation that can address digital crimes. The introduction of stronger data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, is one example of how governments are taking action to address the risks posed by cybercrime.
3. Public Awareness and Education
One of the most effective ways to prevent cybercrime is through public awareness and education. Many cybercrimes are successful because individuals and businesses fail to take basic precautions, such as using strong passwords or being cautious when clicking on links in emails.
Educational campaigns that promote cybersecurity awareness and teach individuals how to recognize and avoid common threats like phishing or ransomware can go a long way in reducing the impact of cybercrime. Governments, organizations, and cybersecurity companies have a role to play in disseminating information on best practices for online safety.
How to Protect Yourself from Cybercrime
Cybercrime is a growing threat, but there are effective steps you can take to protect yourself and your information online. Here are some key strategies:
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
- Avoid common passwords and don’t reuse them across sites.
- Use a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Consider a reputable password manager to keep track of unique passwords securely.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Whenever possible, use 2FA on your accounts. This adds a second layer of security by requiring a code sent to your phone or generated by an app.
3. Be Cautious with Phishing Attempts
- Don’t click on suspicious links in emails, texts, or social media messages, especially from unknown sources.
- Double-check sender information and look for signs of fake URLs or unofficial email domains.
4. Keep Software Up-to-Date
- Regularly update your operating system, browser, and applications, including antivirus software.
- Set updates to happen automatically when possible, as these updates often patch security vulnerabilities.
5. Use Antivirus and Firewall Protection
- Install antivirus software and keep it updated.
- Enable your firewall, as it acts as a barrier between your device and potential attackers.
6. Be Wary of Public Wi-Fi
- Avoid logging into sensitive accounts (like banking) on public Wi-Fi.
- Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when using public Wi-Fi to encrypt your connection.
7. Limit Personal Information on Social Media
- Avoid oversharing details like your address, birthday, or phone number, which can be used in identity theft or to guess security questions.
8. Secure Your Home Network
- Change the default username and password on your Wi-Fi router.
- Use WPA3 encryption, if available, and disable remote access.
9. Monitor Financial and Credit Accounts
- Regularly check your bank statements and credit report to spot unusual activity.
- Sign up for alerts or notifications from your financial institutions.
10. Stay Informed About New Threats
- Cyber threats evolve rapidly, so stay updated on the latest scams and security practices.
- Educate yourself and others, as awareness is a key defense.
By following these precautions, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to cybercrime. Remember, staying vigilant and cautious online is essential for protecting your digital life.
Cybercrime encompasses a wide range of criminal activities that are carried out using digital devices and/or networks. These crimes involve the use of technology to commit fraud, identity theft, data breaches, computer viruses, scams, and expanded upon in other malicious acts. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information, disrupt services, and cause financial or reputational harm to individuals, organizations, and governments

In 2000, the tenth United Nations Congress on the Prevention of Crime and the Treatment of Offenders placed cyber crimes into five categories: unauthorized access, damage to computer data or programs, sabotage to hinder the functioning of a computer system or network, unauthorized interception of data within a system or network, and computer
Internationally, both state and non-state actors engage in cybercrimes, including espionage, financial theft, and other cross-border crimes. Cybercrimes crossing international borders and involving the actions of at least one nation-state are sometimes referred to as cyberwarfare. Warren Buffett has said that cybercrime is the “number one problem with mankind”,[2] and that it “poses real risks to humanity”.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybercrime is a rapidly evolving threat that affects individuals, organizations, and governments worldwide. As technology advances, so do the tactics and tools used by cybercriminals, making it essential for everyone to prioritize cybersecurity measures. This includes adopting strong passwords, being vigilant against phishing attempts, using reliable cybersecurity software, and, at an organizational level, investing in employee training and data protection protocols.

Addressing cybercrime requires a collective effort involving individuals, companies, law enforcement, and governments working together to detect, prevent, and respond to these threats. Stricter laws, international cooperation, and advancements in cybersecurity technology are also crucial to combatting cybercrime effectively. By understanding the risks and committing to proactive security practices, we can create a safer digital environment and reduce the impact of cybercrime on society.
How the Government CyberCrime Website looks
Cyber Crime Government website link – https://cybercrime.gov.in/
Cyber Crime Helpline Number – 1930
National women helpline number – 181
National police helpline number – 112.
