
SEO stands for “search engine optimization” and is the process of improving a website’s visibility and ranking in search engines. The goal of SEO is to help users find a website and decide whether to visit it.
SEO is important because most people use search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo to find information, products, and services. The more visible a website is in search results, the more likely it is to be found and visited.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website or a web page from search engines. SEO targets unpaid traffic (known as “natural” or “organic” results) rather than direct traffic or paid traffic. Unpaid traffic may originate from different kinds of searches, including image search, video search, academic search, news search, and industry-specific vertical search engines.
As an Internet marketing strategy, SEO considers how search engines work, the computer-programmed algorithms that dictate search engine behavior, what people search for, the actual search terms or keywords typed into search engines, and which search engines are preferred by their targeted audience. SEO is performed because a website will receive more visitors from a search engine when websites rank higher on the search engine results page (SERP). These visitors can then potentially be converted into customers.
What is Search Engine Optimization ?

Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of enhancing a website to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). This is achieved through a combination of techniques and best practices that align with search engine algorithms, which determine where a site appears when users search for related terms. Here’s a breakdown of essential SEO components:
1. Keyword Research
- Identifying keywords (phrases or terms) that potential visitors are likely to use in searches is fundamental. Tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush help determine high-value keywords based on search volume, competition, and relevance to your business.
- Focus on long-tail keywords (specific phrases with lower search volume but higher intent) and LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords to broaden content relevance.
2. On-Page SEO
- Title Tags: Optimize each page’s title to reflect primary keywords.
- Meta Descriptions: Write concise, keyword-rich descriptions to improve click-through rates.
- Header Tags: Use H1, H2, H3 tags to structure content; ensure primary keywords appear in H1 and H2 tags.
- Content Quality: Create high-quality, relevant, and valuable content with natural keyword use, internal linking, and multimedia elements.
- URL Structure: Use clean, keyword-focused URLs (e.g., website.com/keyword).
3. Technical SEO
- Site Speed: Optimize loading times, as faster sites rank better.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Google prioritizes mobile-responsive sites.
- Crawlability: Make sure your site’s structure and XML sitemap allow search engines to index your pages easily.
- Security: Secure your site with HTTPS, as Google favors secure websites.
4. Off-Page SEO
- Backlinks: Links from reputable websites signal authority to search engines, enhancing ranking.
- Social Signals: While not a direct ranking factor, social media activity can increase visibility, indirectly improving SEO.
- Guest Blogging and Influencer Marketing: Collaborate with influencers or guest post on high-authority sites to gain exposure and backlinks.
5. User Experience (UX) and Engagement Metrics
- Google’s ranking algorithm increasingly values user experience signals like click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, and bounce rate.
- Design your site for easy navigation and readability, encouraging users to stay longer and interact with content.
6. Local SEO (for Local Businesses)
- Google My Business (GMB): Claim and optimize your GMB profile to appear in local searches.
- NAP Consistency: Ensure your business’s name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent across online directories.
- Local Citations: Build local citations in reputable business directories to improve local visibility.
7. SEO Analytics and Monitoring
- Use tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and third-party software (e.g., Moz, Ahrefs) to monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and track keyword rankings.
What does SEO stand for?
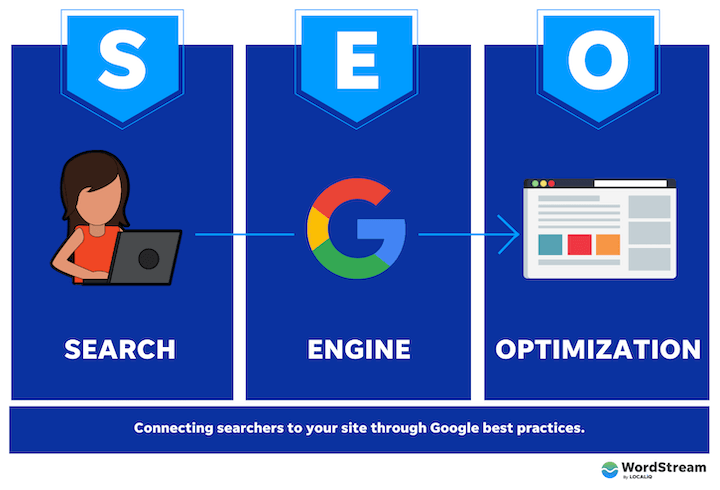
SEO stands for search engine optimization. Let’s break that down in the context of your website.
- Search: What people do when they want to find an answer to a question or a product or service that meets their needs.
- Search engine: A site (like Google or Bing) where a person can perform said search.
- Search engine optimization: What you do to get said search engine to connect said search with your site.
What is SEO?

That’s all well and good, but you can tell me that RPA stands for robotic process automation and that doesn’t mean I know what RPA is.
So what is search engine optimization?
A formal definition of SEO:
Search engine optimization is a set of technical and content practices aimed at aligning a website page with a search engine’s ranking algorithm so it can be easily found, crawled, indexed, and surfaced in the SERP for relevant queries.
A simpler definition of SEO:
SEO is about making improvements to your website’s structure and content so its pages can be discovered by people searching for what you have to offer, through search engines.
The simplest definition of SEO:
SEO is what you do to rank higher on Google and get more traffic to your site.
Yes, Google is just one search engine of many. There’s Bing. Directory search engines. Even Instagram is a search engine. But capturing 92% of the market share, the terms “Google” and “search engine” are synonymous for the intents and purposes of this post.
Key Components of SEO

1. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing individual web pages to improve rankings and earn relevant traffic. It involves the strategic placement of keywords, quality content creation, internal linking, and meta-tag optimization.
- Keyword Research: This is the process of identifying relevant keywords that users search for. Tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can help discover keywords with high search volume and low competition. Keyword research forms the foundation of content strategy.
- Content Optimization: Content is a major factor in SEO. High-quality, informative, and original content that incorporates target keywords naturally can help a page rank well. Content should address users’ needs and be optimized for readability and engagement.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Title tags are HTML elements that specify the title of a web page and should contain target keywords. Meta descriptions provide a summary of the page and can influence click-through rates on SERPs.
- URL Structure: SEO-friendly URLs that include primary keywords and follow a logical structure can improve rankings and user experience. For example, “example.com/seo-tips” is more SEO-friendly than “example.com/?page_id=123.”
- Image Optimization: Images should be optimized by reducing file sizes and using descriptive alt text. Alt text helps search engines understand what the image is about and improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
- Internal Linking: Linking to other pages within the website helps users navigate easily and allows search engines to understand site structure and relevance between pages.
2. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to external activities that improve a website’s reputation and authority. This includes link-building, social media marketing, and other promotional tactics outside the website itself.
- Link Building: Backlinks from reputable websites are a significant ranking factor. Quality backlinks signal to search engines that the website is credible. Effective link-building strategies include guest blogging, influencer outreach, and creating shareable content.
- Social Media Marketing: While social media shares do not directly influence rankings, a strong social media presence can drive traffic and brand awareness, indirectly boosting SEO efforts.
- Brand Mentions: Unlinked brand mentions, which are mentions of a brand without a hyperlink, are increasingly valuable in SEO. They build credibility and send positive signals to search engines.
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures that a website’s infrastructure is optimized for crawling and indexing by search engines. It involves improving site speed, mobile-friendliness, secure connections, and site architecture.
- Crawling and Indexing: Crawling is when search engines visit websites to understand their content, while indexing is the process of storing this information. Tools like Google Search Console help monitor how well a site is crawled and indexed.
- Site Speed: Page load time is a critical ranking factor. Faster-loading pages enhance user experience and reduce bounce rates. Techniques to improve site speed include using caching, compressing images, and minimizing code.
- Mobile Optimization: With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily uses the mobile version of a site for indexing. Ensuring a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes is essential for mobile SEO.
- HTTPS and SSL Certificates: HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP, ensuring data protection. Google favors HTTPS-secured websites, and it is now a ranking factor.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Structured data helps search engines understand the content on a page. By adding schema markup, websites can appear in rich snippets, enhancing their appearance on SERPs and improving click-through rates.
4. Local SEO
Local SEO focuses on optimizing a website to rank for searches specific to a geographic area. It is crucial for businesses with a physical location or those serving a particular locality.
- Google My Business (GMB): GMB is a free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence on Google. An optimized GMB profile can lead to better visibility in local search results.
- NAP Consistency: NAP stands for Name, Address, and Phone number. Consistent NAP information across the website and external directories improves local SEO by building trust with search engines.
- Local Citations: Listings on local directories and review sites help improve local SEO by verifying the business’s presence and reputation.
- Local Keywords: Using local-specific keywords (e.g., “dentist in New York”) helps capture users searching within a particular location.
Benefits & importance of SEO
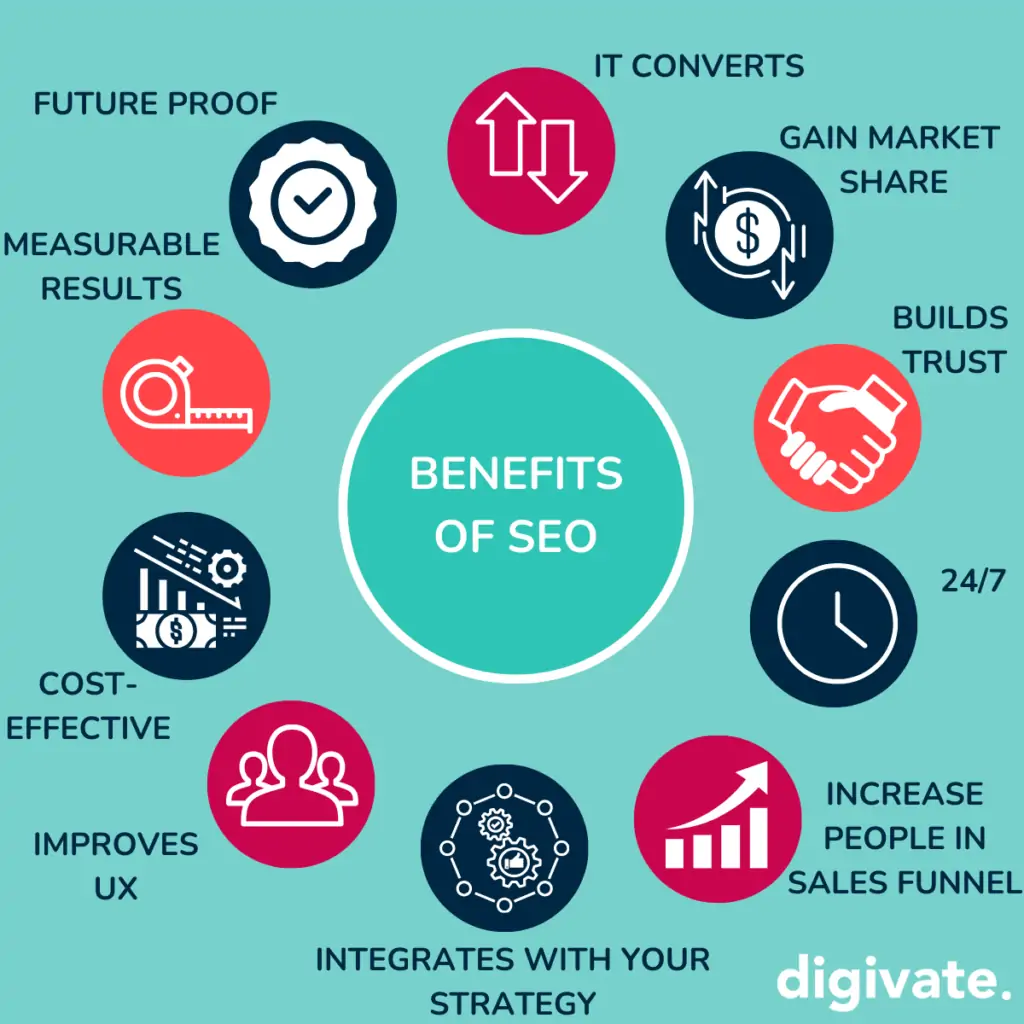
People are searching for any manner of things both loosely and directly related to your business. These are all opportunities to connect with these people, answer their questions, solve their problems, and become a trusted resource for them.
- More website traffic: When your site is optimized for search engines, it gets more traffic which equates to increased brand awareness, as well as…
- More customers: To get your site optimized, it has to target keywords—the terms your ideal customers/visitors are searching—meaning you’ll get more relevant traffic.
- Better reputation: Ranking higher on Google builds instant credibility for your business. If Google trusts you, then people trust you.
- Higher ROI: You put money into your website, and into the marketing campaigns that lead back to your website pages. A top-performing site improves the fruits of those campaigns, making your investment worth it.
So whether you want more brand awareness, online visibility, leads, sales, or loyal customers, SEO is your answer.
SEO is your chance to get in front of potential customers at any stage of their customer journey.
Types of SEO

Google and other search engines take several factors into account when ranking content, and as such SEO has many facets. The core three types of SEO are on-page, off-page, and technical SEO:
- On-page SEO: Optimizing the quality and structure of the content on a page. Content quality, keywords, and HTML tags are the key players for on-page SEO.
- Off-page SEO: Getting other sites, and other pages on your site to link to the page you are trying to optimize. Backlinks, internal linking, and reputation are your off-page MVPs.
- Technical SEO: Improving your site’s overall performance on search engines. Site security (SSL certificates), UX, and structure are key here.
The above three types of SEO are used for websites and blogs, but they also apply to three subtypes of SEO:
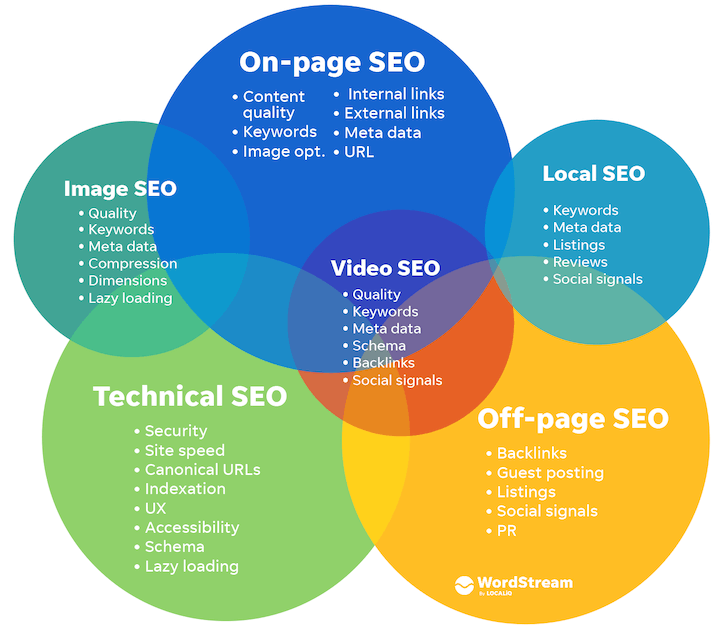
- Local SEO: Getting your business to rank as high as possible in Google Maps and on the local results of the SERP. Reviews, listings, and Google Business profile optimization are most important here.
- Image SEO: A mix of on-page and technical strategies to get images on your website pages to rank in Google image search.
- Video SEO: A mix of on-page, technical, and off-page strategies to get your videos to rank in YouTube or Google video results.
While all three subtypes require all three core types of SEO, they do vary in how heavily they rely on each core type.
Image SEO relies heavily on technical and on-page optimizations while local SEO is more about off-page and on-page optimizations.
How does SEO Work?
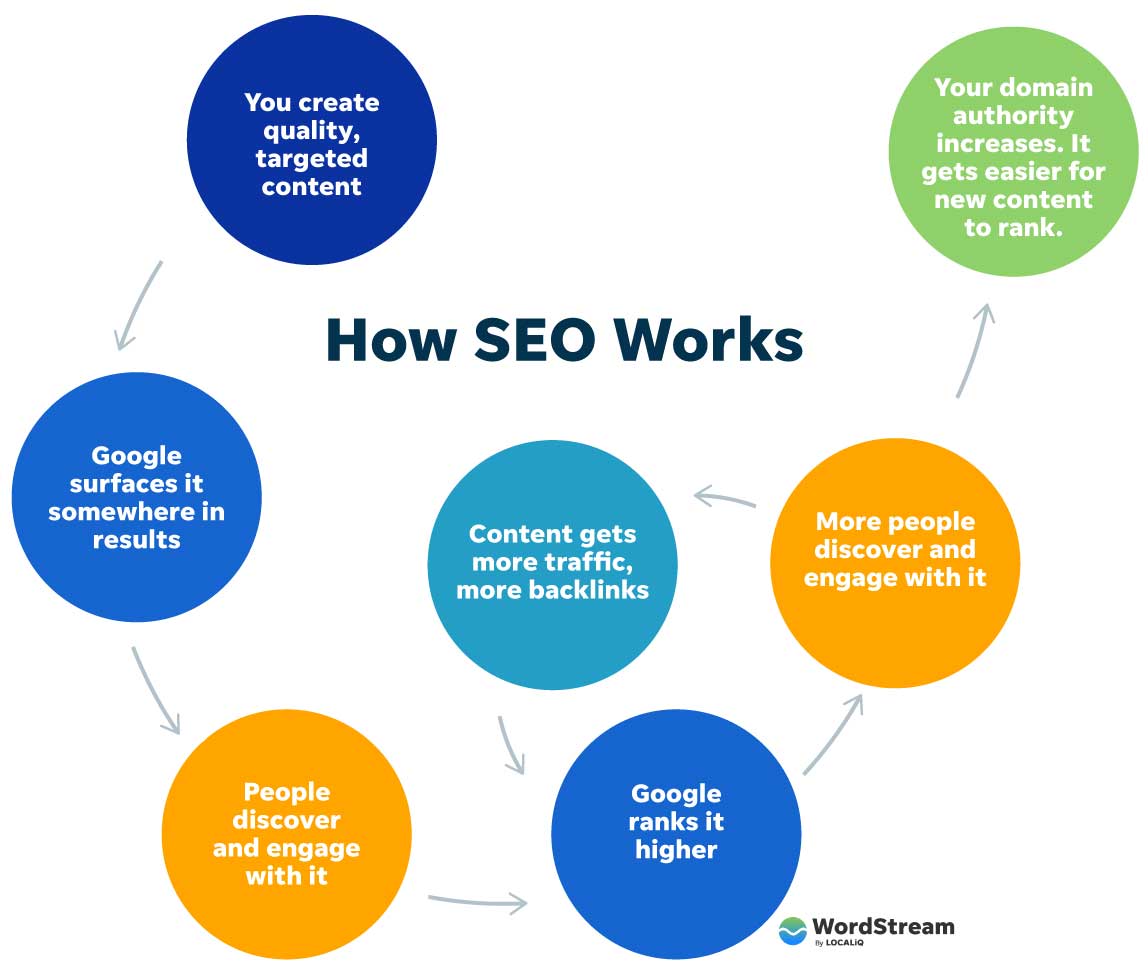
So how does Google determine which pages to surface in the search engine results page (SERP) for any given query? How does this translate into traffic to your website? Let’s take a look at how SEO works.
- Google’s search crawlers constantly scan the web, gathering, categorizing, and storing the billions of web pages out there in its index. When you search for something and Google pulls up results, it’s pulling from its index, not the web itself.
- Google uses a complex formula (called an algorithm) to order results based on a number of criteria (ranking factors—which we’ll get into next) including the quality of the content, its relevance to the search query, the website (domain) it belongs to, and more.
- How people interact with results then further indicates to Google the needs that each page is (or isn’t) satisfying, which also gets factored into the algorithm.
In other words, SEO works like a complex feedback system—to surface the most accurate, trustworthy, and relevant results for any given search using input from you, Google, and searchers. Your role is to produce content that satisfies Google’s experience, expertise, authority, and trust requirements (E-E-A-T), which satisfy its searchers’ requirements.
SEO Tools
You can’t carry out effective search engine optimization without data, and to get data, you need tools. Luckily, most of them are free. The best SEO tools for an optimal SEO strategy are:
- Google Analytics: This is the gold standard for website traffic analytics, and it’s free. Use it for any and all SEO metrics to measure your performance, such as traffic, time on page, engagement with page, number of pages per session, and (lots) more.
- Google Search Console: GSC is essential for content-focused and technical SEO. Although some Search Console data appears in Google Analytics, there is a lot you get in the platform on its own. Use it for Core Web Vitals, granular query analyses, indexing, and more.
- Keyword research tools: As mentioned above, you’ll need these so you can find keywords that are realistic for you to target in terms of search volume and competition. Use my roundup of the best paid and free keyword research tools to find the right one for you.
- SEO software: If you’re going to look at deeper SEO metrics like backlinks, competitive information, and more advanced keyword data, you’ll need a paid SEO tool like Ahrefs, Moz Pro, Screaming Frog, SEMrush, etc. Some of these offer free trial versions or free services for the first 500 (or something) links.
- Website graders: Whereas the aforementioned tools are often complex and require you to know how to make sense of the data, website graders can simplify SEO for you and offer more guidance.
Head here to get an instant SEO audit with our Free Website Grader.
SEO Best Practices

Let’s finish off with some SEO strategies, best practices, and tips to help you get the most out of your time.
- Always always search the keyword: What you think users are looking for when they perform a particular search in Google may not be what they’re actually looking for. Keyword intent matters, so always search the keywords you’re trying to target to make sure you have an intent match.
- Be patient: SEO takes time. Like, a lot of time. It can take a few months before you really start to see the fruit of your efforts, but once you start seeing the impact, the benefits compound over time—so don’t give up prematurely!
- Focus on quality: Google is always updating its algorithm and coming out with new SERP features, but at the end of the day, it’s all designed to surface the best content out there. So your focus should always remain on creating useful, trustworthy content consistently. That is the best SEO strategy above all else.
- Maintain your content: While the consistent publication of quality content is the top Google ranking factor, this should not be at the expense of letting old content go stale. Regularly refresh your evergreen pages to preserve their SEO value and get consistent traffic growth over time.
- Track and measure: Report on your traffic and site data regularly so you can see what topics resonate most with your audience, detect issues, and set goals for traffic growth.
Advanced SEO Strategies

1. User Experience (UX) Optimization
Improving UX can have a positive impact on SEO as search engines increasingly prioritize user engagement metrics.
- Page Layout and Design: A clean, easy-to-navigate design enhances UX and reduces bounce rates.
- Core Web Vitals: Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics focusing on loading, interactivity, and visual stability. Optimizing these metrics can improve rankings.
- Dwell Time: Dwell time is the amount of time a user spends on a page. Content that keeps users engaged can increase dwell time, signaling to search engines that the page is relevant and valuable.
2. Content Strategy and E-A-T
E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Google uses E-A-T to evaluate the quality of content, especially in sensitive topics like health, finance, or news.
- Authoritative Content: High-quality content that is informative, well-researched, and reliable can improve E-A-T. Adding author credentials can boost credibility.
- User-Generated Content: Engaging users to generate content, such as reviews and comments, adds to the page’s authority and relevance.
- Content Refreshing: Updating existing content with recent information can keep it relevant and improve rankings.
3. Voice Search Optimization
With the rise of smart speakers and voice-activated devices, voice search optimization is becoming essential.
- Natural Language Keywords: People use conversational language in voice searches, so optimizing for long-tail keywords and question-based phrases can improve voice search rankings.
- Featured Snippets: Optimizing for featured snippets can improve voice search performance, as these are often read aloud in voice search results.
4. Video SEO
Video content is gaining importance in SEO as search engines increasingly prioritize rich media.
- Optimized Titles and Descriptions: Titles and descriptions should be informative and include keywords. Adding transcripts can improve accessibility and SEO.
- Video Thumbnails: Custom thumbnails that are visually engaging can improve click-through rates.
- Embedding Videos: Embedding videos on relevant pages keeps users engaged and can boost rankings.
5. International SEO
For businesses operating globally, international SEO helps ensure content is accessible to different languages and regions.
- Hreflang Tags: These tags tell search engines which language the page is in and the target region, preventing duplicate content issues across different languages.
- Country-Specific Domains: Using country-code top-level domains (e.g., “.uk” for the UK) can improve visibility in local searches.
Measuring SEO Performance

Tracking SEO performance is essential for ongoing optimization. Key metrics to monitor include:
- Organic Traffic: Measures the number of visitors who found the site via organic search.
- Keyword Rankings: Shows the position of target keywords on SERPs.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave after viewing one page; a high rate may indicate issues with content or UX.
- Conversion Rate: Measures how well organic traffic converts into leads or sales.
- Backlinks: Quantity and quality of inbound links, as they indicate site authority.
- Page Load Time: Time taken for the page to load, impacting UX and SEO.
Tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, Ahrefs, Moz, and SEMrush can provide insights into these metrics, helping businesses adjust their strategies.
Advantages of SEO

- Increased Visibility and Traffic: SEO improves a site’s ranking, bringing in more organic traffic from search engines, often translating into more leads, conversions, or brand awareness.
- Cost-Effective Long-Term Strategy: Once established, SEO can be a cost-effective way to maintain traffic without ongoing ad spend, unlike PPC campaigns that require continuous funding.
- Enhanced Credibility and Trust: Higher rankings and optimized content often make a business appear more trustworthy and credible to users.
- Improved User Experience: SEO practices encourage faster page load times, mobile optimization, and improved navigation, making websites more user-friendly.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective SEO can help a brand stay ahead of competitors in terms of visibility and reach, especially in a niche market.
- Local Reach Optimization: With local SEO, businesses can target users in specific locations, which is highly beneficial for brick-and-mortar businesses and local service providers.
Disadvantages of SEO
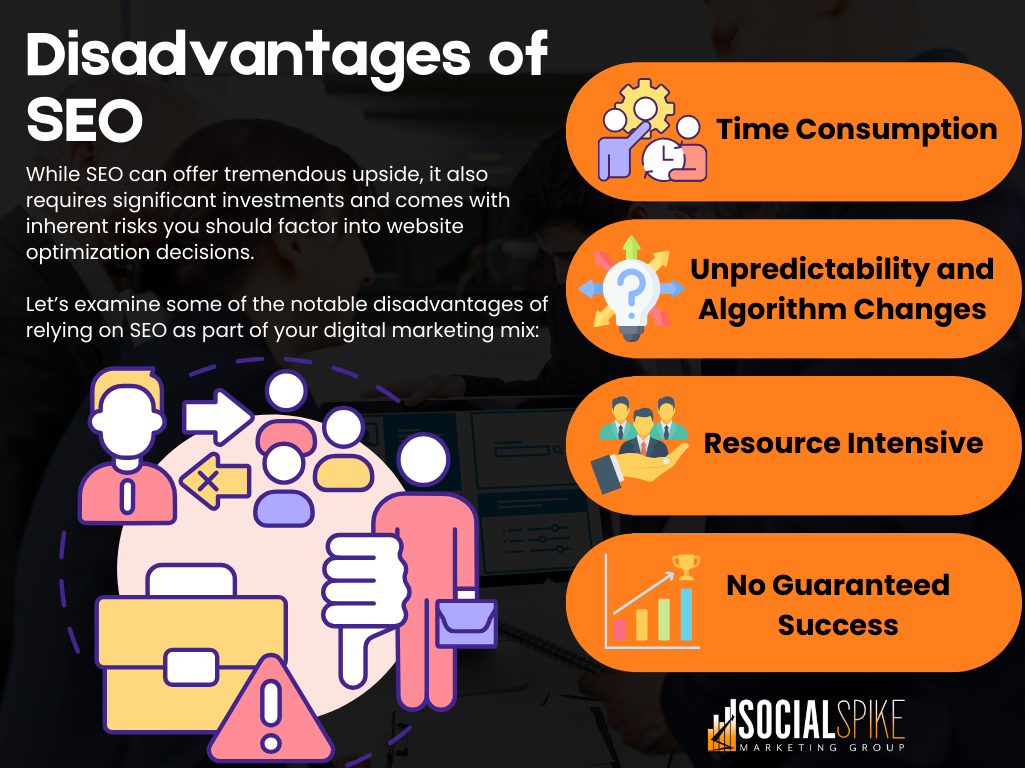
- Time-Consuming: SEO is not an immediate solution. It may take several months or even longer to see significant results, especially for new websites.
- Uncertain Results: SEO efforts do not guarantee top rankings, as they are subject to frequent changes in search engine algorithms.
- Algorithm Dependency: Search engine algorithms are updated regularly, which can impact a website’s ranking unpredictably, leading to potential loss of traffic.
- High Competition: In competitive industries, SEO can be challenging due to the high number of players all trying to rank for the same keywords.
- Ongoing Maintenance: SEO requires regular updates to keep content relevant and optimized. Failure to adapt can lead to a drop in rankings.
Limitations of SEO
- Limited Control Over Rankings: SEO success is partially dependent on factors beyond control, such as algorithm changes and competitor actions.
- Content Saturation: In crowded niches, it’s challenging to rank without creating exceptionally unique content, as many other sites are optimized similarly.
- Limited Impact for Short-Term Goals: SEO is better suited for long-term gains rather than immediate results. Short-term campaigns or promotions might not benefit much from SEO alone.
- Highly Dependent on Quality Content: SEO is reliant on high-quality, regularly updated content, which can be resource-intensive to maintain.
- Potential for Negative SEO: Malicious competitors can use “negative SEO” tactics, like spammy backlinks or duplicated content, to harm a site’s rankings.
Conclusion

While SEO has notable advantages as a sustainable, cost-effective way to drive organic traffic and build brand authority, it also comes with time investment, competition, and the need for constant updates to stay competitive.
In conclusion, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) remains a vital component of digital marketing, enabling websites to enhance their visibility in search engine results and attract organic traffic. Effective SEO involves a balanced approach that incorporates on-page strategies, like optimizing keywords, metadata, and content quality, as well as off-page tactics, such as backlinks and social signals. Technical SEO, including site speed and mobile responsiveness, is also crucial, as it directly impacts user experience and search engine rankings.
The SEO landscape continually evolves with search engine algorithm updates, particularly from Google, which emphasizes user-centric metrics like content relevance, engagement, and website security. Therefore, keeping up-to-date with these changes and focusing on creating valuable, user-focused content is essential.
Overall, SEO is a long-term strategy that requires consistent effort and adjustment to maintain high rankings and visibility. By integrating SEO best practices, businesses can increase their online reach, improve user engagement, and, ultimately, drive conversions and growth.
